What Does the Vsepr Theory Tell About a Molecule Apex
Advertisement Advertisement New questions in Chemistry. It is based on the assumption that the molecule will take such a shape that will minimize electronic repulsion in the valence shell.
7 6 Molecular Structure And Polarity Chemistry
The VSEPR theory is used to predict the shape of the molecules from the electron pairs that surround the central atoms of the molecule.
. The shape of a molecule. It is a fact that electron pairs arranged around a. The VSEPR theory is a tool that is used for predicting the shape of a molecule from the electron pairs that surround the central atoms of that molecule.
The electrons are attached. Using the VSEPR theory the electron bond pairs and lone pairs on the center atom will help us predict the shape of a molecule. The lone pair occupies space around nitrogen atom just as the bonding pairs do what does the shape of the molecule refer to.
VSEPR models are based on the concept that electrons around a central atom will configure themselves to minimize repulsion and that dictates the geometry of the molecule. This is determined by VSEPR theory -When the central atom doesnt have any lone pairs the molecular geometry and the electron domain geometry have the same name when the central atom does have lone pairs the molecular geometry name is different. According to vsepr theory the repulsion between electron pairs causes molecular shapes to adjust so that the valence electron pairs stay as far apart as possible are unshared pairs important in predicting the shapes of molecules.
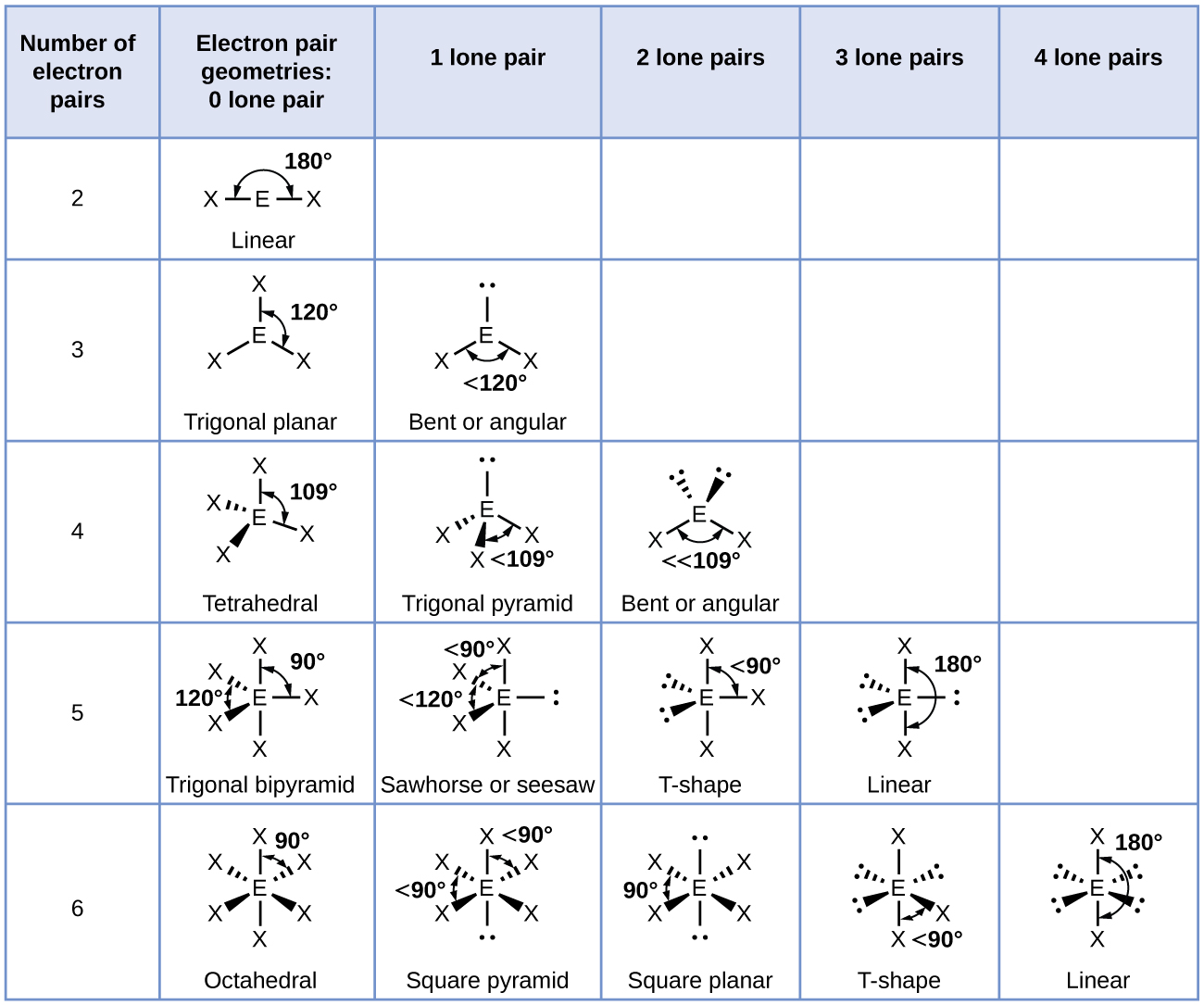
The theory was given by Sidgwick and Powell in the year 1940. The five compounds shown in the figure below can be used to demonstrate how the VSEPR theory can be applied to simple molecules. Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory VSEPR theory enables us to predict the molecular structure including approximate bond angles around a central atom of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structure.
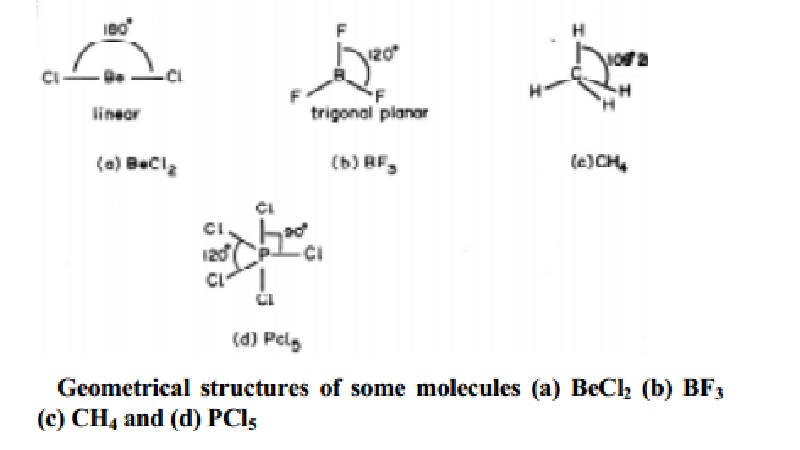
VSEPR counts the number of electron pairs around a central atom both bonding and non-bonding and assigns a shape according to the Platonic solids. When the two electron groups are 180 apart the atoms attached to those electron groups are also 180 apart so the overall molecular shape is linear. 1 Beryllium hydride and carbon dioxide bonding.
Using this theory you can determine what shape a molecule will take in three-dimensional space including both electron domain geometry and molecular geometry. It can predict the shape of nearly all compounds that have a central atom as long as the central atom is not a. The VSEPR model combines the original ideas of Sidwick and Powell and further development of Nyholm and Gillespie.
Examples include BeH 2 and CO 2. Linear molecule A simple triatomic molecule of the type AX2 has its two bonding orbitals 180 apart producing a molecule of linear geometry. The central carbon atom is still joined to two other atoms and the electron clouds that connect the two oxygen atoms are 180 apart.
The shape of a molecule is determined by the location of the nuclei and its electrons. The 3-D shape of the molecule. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory vesper for short classifies molecules on the basis of the number of electron pairs bonding and lone pairs associated with the central atom.
Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory VESPER for short. Each group around the central atom is designated as a bonding pair BP or lone nonbonding pair LP. The two molecules shown in the figure below in a ball and stick model.
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory. VSEPR - Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory predicts the shape of a molecule. Advertisement Advertisement correatp0525 correatp0525 Answer.
What does the VSEPR theory postulate. See this older answer. The VSEPR theory is based on the assumption that the molecule will take a shape such that electronic repulsion in the valence shell of that atom is minimized.
The electrons and the nuclei settle into positions that minimize repulsion and maximize attraction. You can also predict _____ _____ and _____ _____ by using VSEPR Theory. There are only two places in the valence shell of the.
11212021 Create an account. The VSEPR theory assumes that each atom in a molecule will achieve a geometry that minimizes the repulsion between electrons in the valence shell of that atom. The shape of a molecule is determined by the repulsion of electron pairs.
The shapes of the molecules is determined mainly by the electrons surrounding the central atom. In the VSEPR model the molecule or polyatomic ion is given an AX m E n designation where A is the central atom X is a bonded atom E is a nonbonding valence electron group usually a lone pair of electrons and m and n are integers. A P E X.
The theory was first presented by Sidgwick and Powell in 1940. This makes no difference to VSEPR theory. Therefore VSEPR theory gives simple directions on how to predict the shape of the molecules.
Steps for using VSEPR Theory-draw a lewis dot diagram-predict the geometry around the central atom-name the molecular shape. The shapes of molecules can be predicted from their Lewis structures by using a model developed about 30 years ago known as the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion VSEPR theory-The VSEPR concept revolves around the idea that the electrons in a molecule repel each other and will try to get as far away from each other as possible.

6 3 Molecular Shape Introductory Chemistry

0 Response to "What Does the Vsepr Theory Tell About a Molecule Apex"
Post a Comment